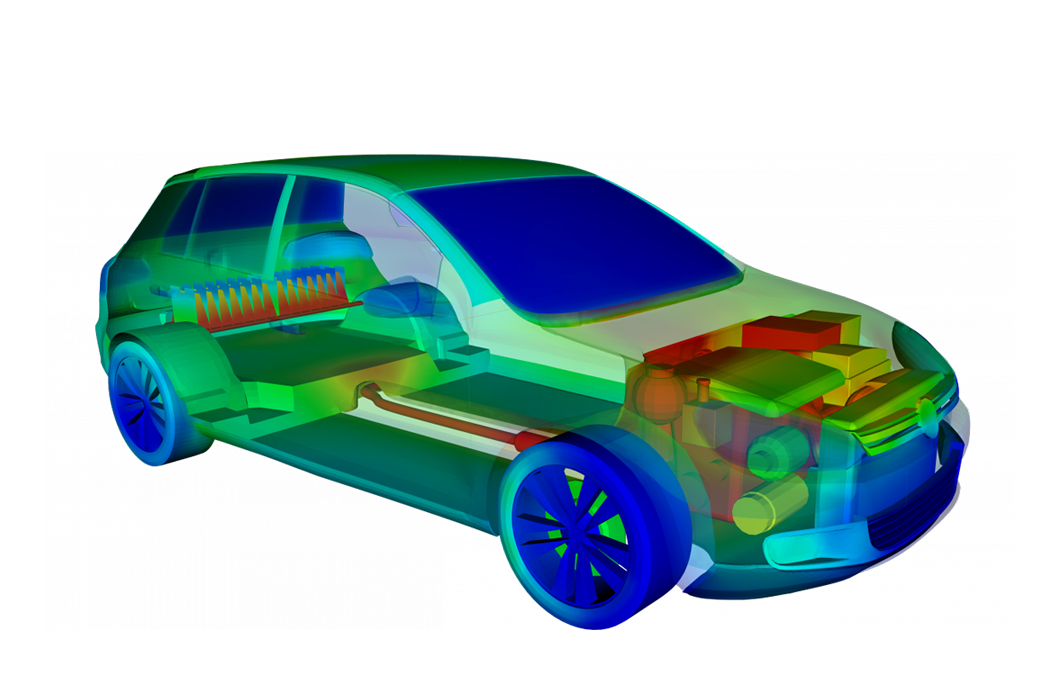
Predicting fluid flow rates, pressure drops, and turbulence are few challenges during the initial phase of design. Understanding these performance indicators with the use of CFD simulation enables engineers to explore more ideas and make better design decisions for internal/external flows.
In the automotive and aerospace industries, thermal management is necessary for heat protection of the components. Transient Thermal analysis methods are important for analyzing the drive cycle simulation considering the environmental effects for batteries, exhaust, cabin comfort and Underhood /Underbody.
Xitadel can help in assessing and optimizing the design for improved efficiency in fluid flow and help you in understanding the source of heat, its effect on the different subsystem and optimizing the heat shield with different cooling strategies. Xitadel is best placed to offer innovative solutions in the area of CFD/Thermal Management spanning Vehicle Thermal Management to IR Simulations by employing the latest technologies to help implement innovative solutions leveraging its partnerships with niche technology partners.
CFD allows you to simulate almost any engineering problems that involves the flow of liquid and gases or combination of both, together with all the associated physics. Following are our expertise in the CFD domain.
Reducing drag and wind noise, minimizing noise emission, and preventing undesired lift forces and other causes of aerodynamic instability at high speeds. Further studies can be extended through vehicle dynamics on crosswind lateral stability, longitudinal dynamics and fuel consumption.
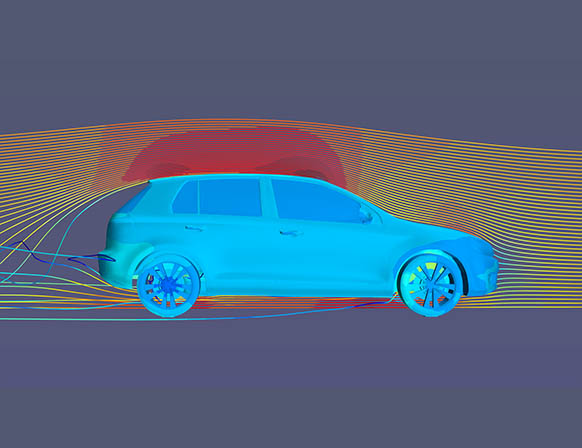
The efficiency of the vehicle cooling system strongly depends on the air flow through the radiator core. The flow through the radiator core in turn depends on other panels that are in the vicinity of the radiator. The effect of geometrical change at vehicle front-end including the whole bonnet, grille and bumper area is investigated by means of CFD.
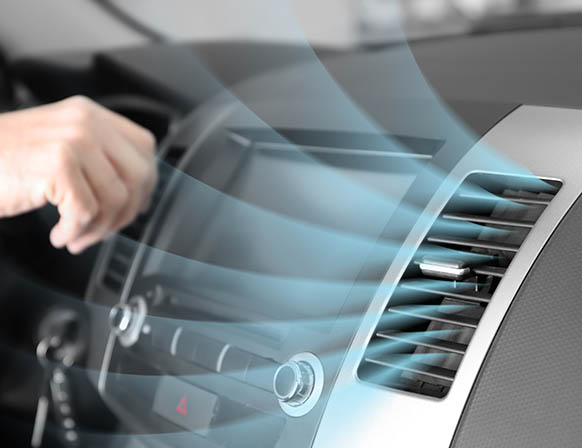

Aims to simulate the airflow inside a car cabin. Improved cabin design will ensure both the driver and the passenger’s thermal comfort. Our goal is to observe the velocity and temperature contours to study the airflow pattern and the heating and cooling regions.
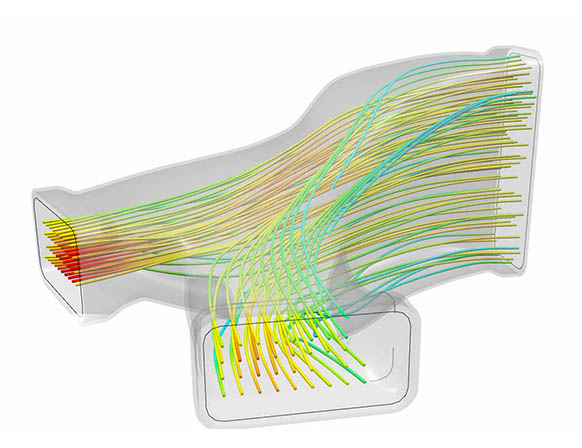
Pressure forces exerted on valve components during operation are essential to both product performance and life lifetime. Engineers and designers may use fluid flow simulation to detect flow features such as high-pressure areas, allowing them to make knowledgeable design decisions. CFD assists in the identification and elimination of these pressure differences.
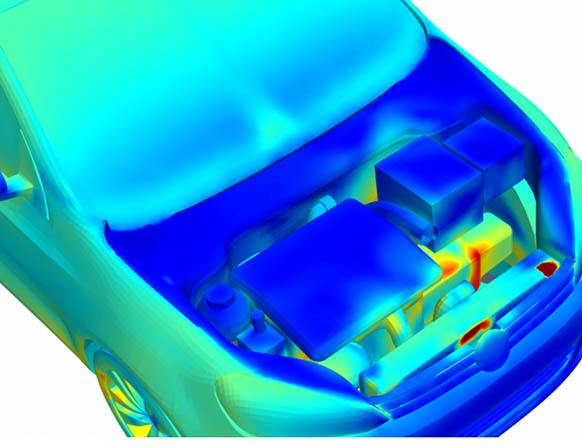
Transient component temperatures for the vehicle under-hood and underbody are estimated. The main focus is on the component temperatures as a result of radiation from exhaust, convection by underbody or under-hood air and heat conduction through the components.
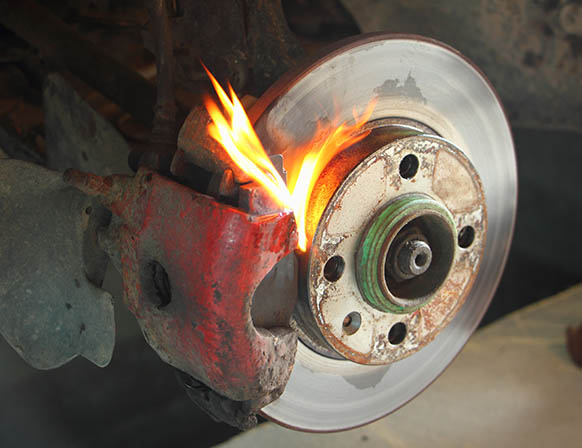

Brake Thermal modeling examines the thermal behavior of the full and ventilated brake discs of the vehicles. Modeling of the temperature distribution in the disc brake to identify all the factors and the entering parameters concerned at the time of the braking operation such as the type of braking, the geometric design of the disc and the used material.
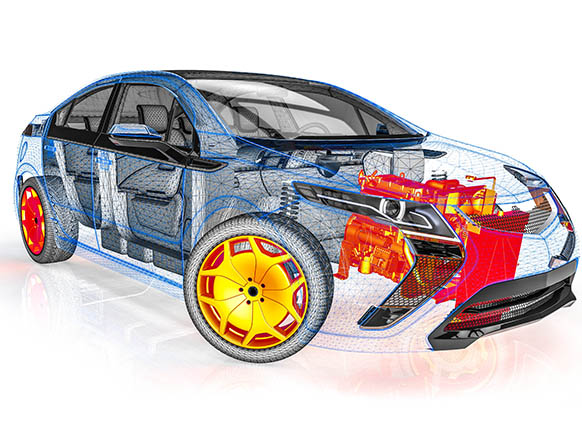

Lately, packaging constrictions dominate the positioning and organization of components within the engine compartment. With less space and more temperature-sensitive elements, (plastics for lightweighting, infotainment, and electrical components) thermal management becomes an increasingly critical aspect of vehicle design. Component hot spots can lead to safety, durability and warranty issues. Careful consideration of component placement and heat shields is mandatory to avoid costly late-stage fixes.
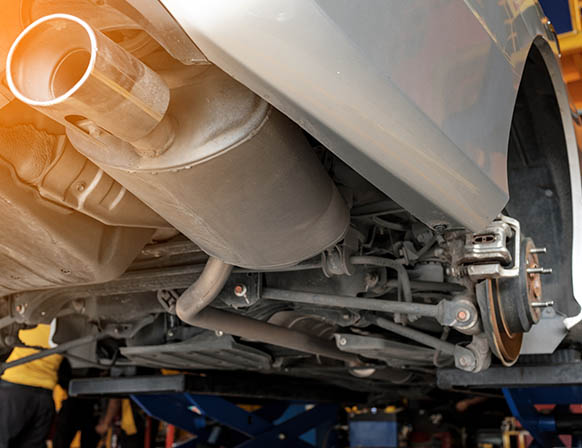

The automotive exhaust system is exposed to high temperature as the hot gases from combustion chamber passes through it. The uniform distribution of heat is needed to enhance life of exhaust system components. Heat transfer studies in the exhaust system is necessary to understand the physical phenomena takes place in it which is required to design purpose of exhaust system.
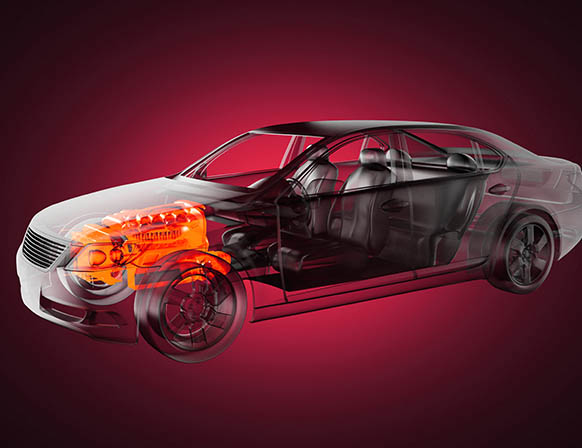

One of the greatest intense scenarios for thermal stress is "key-off/soak" where a vehicle with a red-hot engine rapidly goes to a halt and low temperature rises because there is no cooling air flow. In order to avoid costly late-stage design fixes or worse, failures when in production, careful and detailed analysis of the component placement and thermal shielding is required.
Vehicle Thermal Management is important aspect of CAE and it involves solving Complex thermal management challenges, identifying the source of heat generation and managing it dissipation.
Predict human thermal comfort, safety and effectiveness is key to customer experience. It is also major challenge of OEM’s to manage the comfort level for different types of Vehicle under different environmental conditions.
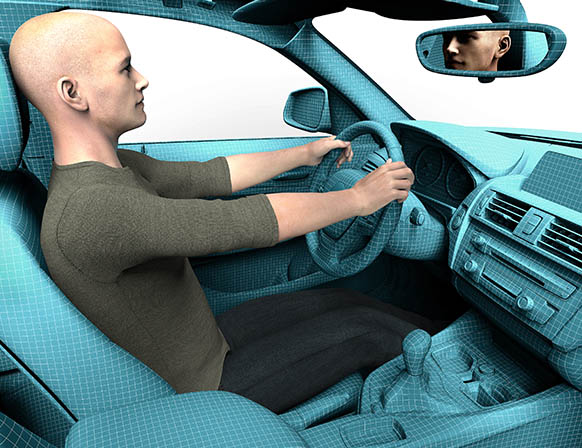

In the area of Multiphysics like car cabins are non-uniform and asymmetric environments in relation to both air velocity and temperature. Estimating and controlling vehicle occupant thermal comfort is therefore a challenging task. Analysis and modeling of vehicular thermal comfort parameters using a set of designed experiments to accurately assess the transient and steady state temperature distributions of the test vehicle cabin.
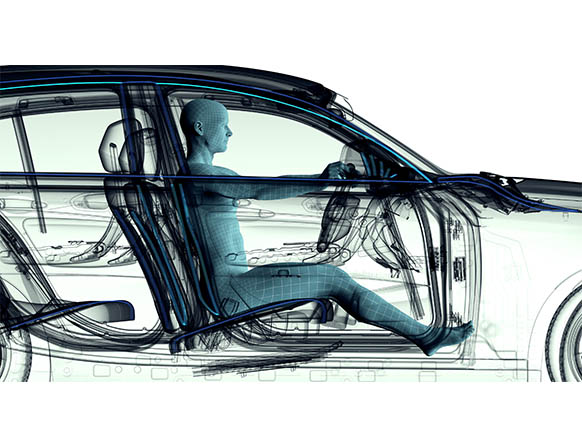
Taking into account factors such as room temperature, humidity and expected occupancy, as well as heat loss through doors, windows and walls, the development of HVAC systems to maximize thermal comfort Modeling the flow of air in a structure is key to the best design of an HVAC system

The heat exchange of humans with the surroundings during cabin heat-up is taken into consideration to reproduce the realistic test scenario. Transient temperature distribution inside the cabin along with thermal sensation and comfort prediction of multiple humans is studied.
Evaluate the performance, life, and cost of battery pack designs for the entire service life of the pack. Lifetime Model describes relative capacity and relative internal resistance as functions of time and number of cycles. Understand how your design effects lifetime and performance in terms of age and decline in performance due to cycling fade. We can accurately describe degradation for your battery lifetime model.
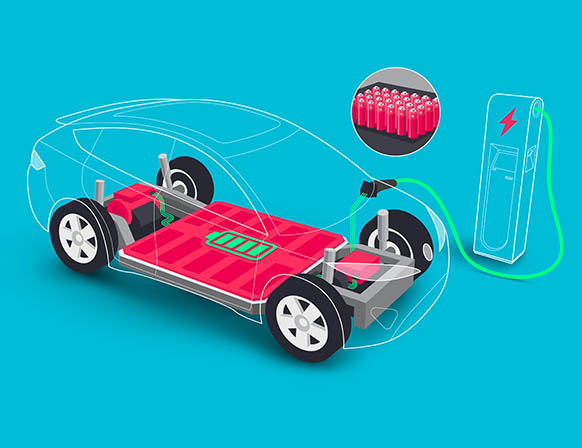
Control of heat generation and dissipation. Cooling methods for heat removal. Design methods for avoiding fault propagation.
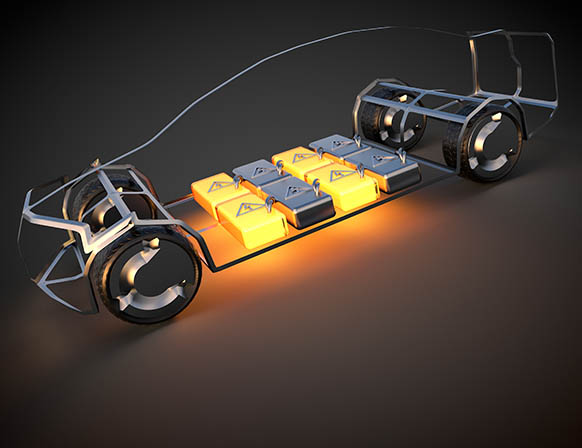
Thermal runaway occurs when a cell, or area within the cell, attains elevated temperatures due to thermal failure, mechanical failure, internal/external short circuiting, and electrochemical abuse. Understanding the causes of thermal run away and making the proper design and cooling methods.

Understanding the source of internal heat generation and designing a system that cools all of the batteries uniformly leads to better battery performance and lifetime.
Take charge of your battery-powered design
Accurate assessments. Actionable intelligence.
Sensor at any range, lookdown angle, and azimuth, whether at short range near ground or from aerial and satellite platforms. The source radiance is then spectrally attenuated back to the sensor location. Easily script up multiple ranges and LOS’s to build a complete library of band-specific contrast values.

Often probability of detection (POD) is computed for numerous ranges from target to sensor. To test low observables designs, examine operational profiles for vulnerable, high-contrast situations, and even plan the best times for execution.

Observing individuals, ships, vehicles, and aircraft on the ground from satellites and aerial platforms requires accurate atmospheric attenuation along the sensor line of sight. MODTRAN, the benchmark for physics-based atmospheric radiance computations, along with weather data and solar intensity to yield accurate renderings of ground-based assets. Solar loading, thermal shadows, and thermal lag are all computed over long time periods to accurately capture the temperature distribution and source radiances for the sensor wave band. Rendering with multi-bounce ray tracing yields physically accurate and realistic contrast metrics.
Using texture mapping, remote imagery can be used to impose a temperature distribution on terrains. This enables you to drive an aerial scenario with realistic terrain temperature distribution on a faceted background component. Targets can be placed on the terrain and rendered against complex, cluttered backgrounds.
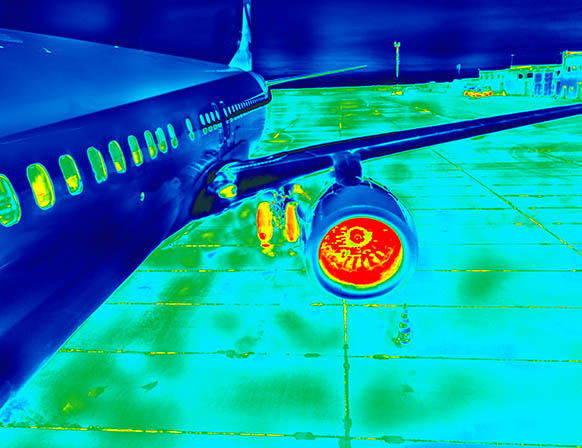
Many EO/IR signature challenges are rooted in thermal behavior, accurately simulating heat transfer and can thus be a virtual test platform for low observables kits or primary system analysis.
As a trusted partner, you can depend on Xitadel to provide outstanding value to your organization in all areas of World Class Technology, Expertise and Consulting.